
By David A. Wheeler
Many open source software (OSS) projects aim to securely develop software and have an easy way to communicate their security posture to others.
Overview
The OpenSSF developed the Open Source Project Security Baseline (OSPS Baseline) to act as a “minimum definition of requirements for a project relative to its maturity level”. It’s a three-level checklist (baseline-1 through baseline-3) to help OSS projects improve their security. The OpenSSF Best Practices Badge Program now supports the baseline criteria, making it easier for OSS projects to determine what they’ve already accomplished and what remains. OSS projects can then display their badge on their web pages, demonstrating what they’ve accomplished and making it easy for potential users to learn more.
This post introduces how to earn an OpenSSF baseline badge through the OpenSSF Best Practices Badge System.
Getting Started with the Best Practices Badge Program
First, visit https://www.bestpractices.dev. The site currently supports nine locales, and this URL automatically redirects you to your preferred language (e.g., https://www.bestpractices.dev/en for English).
Click on “Login” to add information. You can use your GitHub account to log in. Most users prefer this method. You must grant permission during your first visit. You can also create an account specifically for the site.
Click on the “Projects” tab to see projects currently pursuing badges, then click either the “+ Add” tab or the “Add New Project” button. The “New badge” form allows you to enter your project’s repository URL and/or home page URL. You can also decide whether to begin with the “metal” series or the “baseline” series. The baseline series is a focused checklist that includes only MUST security requirements and draws in part from global cybersecurity regulations and frameworks. The metal series is a larger set of criteria that includes suggestions and quality issues impacting security derived in part from the experiences of secure Free/Libre and Open Source Software (FLOSS) projects. Both focus on security, and we encourage projects to eventually complete both; simply choose a starting point. For the purposes of this blog post, we’ll assume you chose the “baseline” series.
When you click on “Submit Project”, the system assigns a unique numeric ID to the project. The system will pause to examine the repository and attempt to automatically determine the answers to various questions. For many, this automation can save a lot of time. Once that’s done, you’ll see a form to update project information. Information highlighted in yellow with the robot symbol 🤖 indicates data entered by automation. We recommend double-checking automation results for accuracy.
 Understanding and Completing the Baseline Criteria
Understanding and Completing the Baseline Criteria
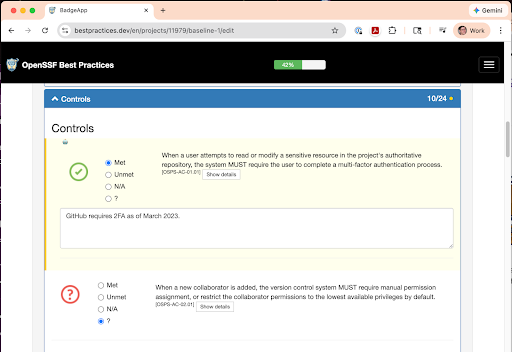
You can now fill in the form. Each criterion can be “?” (unknown), “N/A” (not applicable), Unmet, or Met. By default, each is marked “?” (unknown). As you identify more and more items that are Met (or N/A), the % completion bar will increase. We’ve intentionally gamified this; when you reach 100% in baseline-1, you’ve earned a baseline-1 badge. You can also provide justification text; we recommend including it (even when it’s not required) to help others understand the project’s current status. Badge claims are mostly self-assertions. In some cases, automation can override false claims. The answers given are presented for public scrutiny, incentivizing correct answers.
The form shows the criterion requirements; click “show details” for more information. For example, baseline-1 criterion OSPS-AC-01.01 requires that, “When a user attempts to read or modify a sensitive resource in the project’s authoritative repository, the system MUST require the user to complete a multi-factor authentication process.” Any project hosted on GitHub automatically meets this requirement. GitHub has required multi-factor authentication since March 2023, and the system automatically fills in the required information. Not all projects are hosted on GitHub. Those projects must ensure they meet this criterion.
When you’re done, you can select “Save and Continue” or “Save and Exit” to save your work to the website. The “Save and Continue” option not only lets you continue, but also reruns automations to fill in currently unknown information.
The Best Practices Badge site currently supports version v2025.10.10, but it will soon integrate the recently released v2026.02.19. New requirements wil initially appear as “future” criteria, allowing maintainers to address updates without losing their current badge status. There is no reason to wait; projects should begin the process now, as the system will provide ample time to adapt to new criteria.
Displaying Your Baseline Badge
Once you’ve met the baseline-1 criteria, you can add some code to your repository to show off your badge. The site shows the code to add, and it follows the usual badge conventions. For example, in Markdown you would add this:
[]
(https://www.bestpractices.dev/projects/ID)
If you’ve earned the baseline-1 badge, this Markdown code would show an image like this:
Advanced Integrations and Automation Options
We support various mechanisms to rapidly get information in and out of the badge system (replace “ID” with the project’s numerical ID), for example:
- Project’s information (JSON): https://www.bestpractices.dev/projects/ID.json
- Project’s baseline badge (SVG) https://www.bestpractices.dev/projects/ID/baseline
- Proposed edit values: https://www.bestpractices.dev/projects/ID/SECTION/edit?PROPOSALS where PROPOSALS is &-separated key=value pairs. This highlights those proposals with a robot icon, so you can review them before accepting them. For example, in section “baseline-1” you can use the proposal “osps_ac_01_01_status=met” to propose setting the status of OSPS-AC-01.01 to “Met”. For more information, see the documentation on automation proposals.
You can also include a “.bestpractices.json” file in the repository that contains proposed values for a badge. If present, these values will be treated as automation results and highlighted during editing so users can decide whether or not to accept them. The .bestpractices.json documentation provides more details.
Why the Baseline Badge Matters
Our goal is to help OSS projects identify next steps to improve security and provide clear guidance. These capabilities help projects demonstrate measurable progress.
If you maintain an OSS project, visit https://www.bestpractices.dev and start working on a badge. If you use OSS, support those projects on which you depend as they strengthen their security practices.
About the Author
 Dr. David A. Wheeler is an expert on developing secure software and on open source software. He created the Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) courses “Developing Secure Software” (LFD121) and “Understanding the EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA)” (LFEL1001), and is completing creation of the OpenSSF course “Secure AI/ML-Driven Software Development” (LFEL1012). His other contributions include “Fully Countering Trusting Trust through Diverse Double-Compiling (DDC)”. He is the Director of Open Source Supply Chain Security at the Linux Foundation and teaches a graduate course in developing secure software at George Mason University (GMU).
Dr. David A. Wheeler is an expert on developing secure software and on open source software. He created the Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) courses “Developing Secure Software” (LFD121) and “Understanding the EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA)” (LFEL1001), and is completing creation of the OpenSSF course “Secure AI/ML-Driven Software Development” (LFEL1012). His other contributions include “Fully Countering Trusting Trust through Diverse Double-Compiling (DDC)”. He is the Director of Open Source Supply Chain Security at the Linux Foundation and teaches a graduate course in developing secure software at George Mason University (GMU).








