
On September 24, the Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) hosted its latest Tech Talk, bringing together experts from Dell, Google, Intel, and the broader community to discuss how open source tools and practices can secure the fast-evolving AI/ML lifecycle. The recording and slides are now available.
Setting the Stage
The session focused on the “three T’s” of AI security in open source: Trust, Transparency, and Tooling. Speakers explored how existing DevSecOps practices can extend to machine learning systems while addressing unique risks introduced by data, models, and pipelines.
Panelists included:
- Sarah Evans (Dell Technologies) – Distinguished Engineer, presenting the new Visualizing Secure MLOps (MLSecOps) whitepaper.
- Mihai Maruseac (Google) – OpenSSF AI/ML Security Working Group lead, discussing model signing and AI supply chain risks.
- Marcela Melara (Intel Labs) – Research Scientist, sharing emerging work on provenance, trusted execution, and GPU-based integrity.
Key Highlights
- Visualizing Secure MLOps Whitepaper
Sarah introduced a practical guide that adapts DevSecOps practices to AI/ML pipelines. The paper defines roles, risks, controls, and tools, offering a visual reference architecture for securing machine learning operations.
- Model Signing for AI ArtifactsMihai described how model signing extends beyond traditional artifact signing to address multi-format, distributed ML workflows. Integrations with Kaggle and NVIDIA Model Hub already show signed models in action, enabling cryptographic provenance across training, fine-tuning, and deployment.
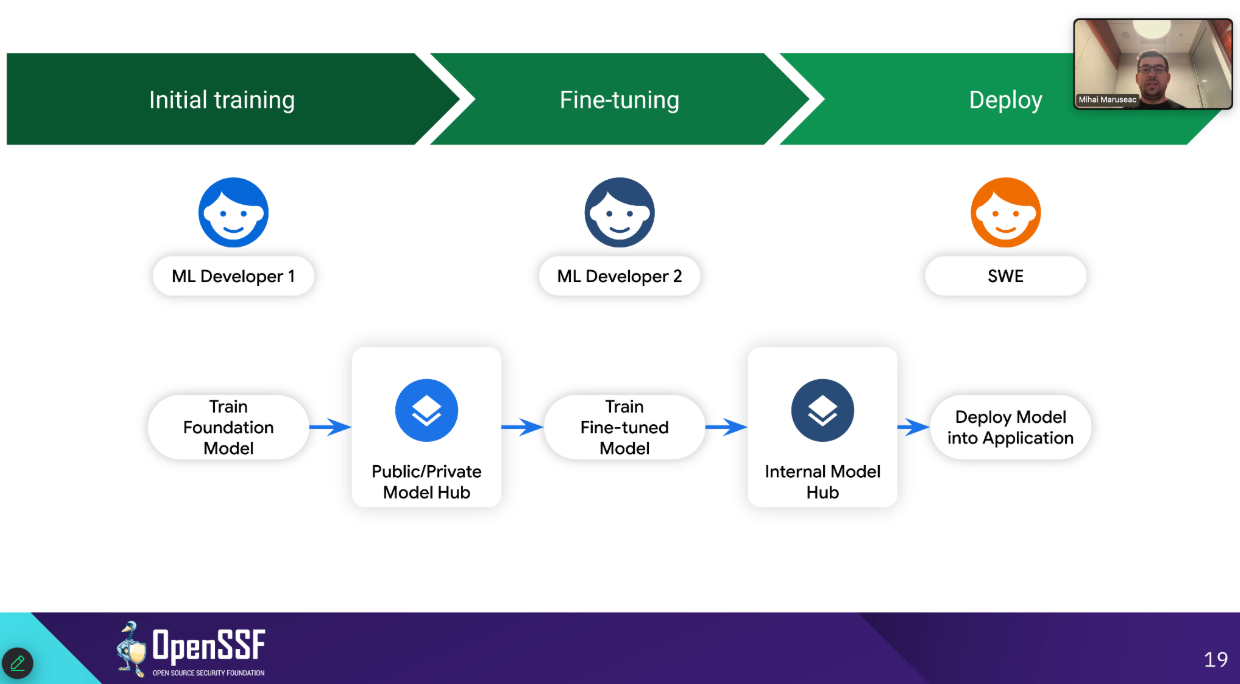
- Atlas: End-to-End Provenance
Marcela shared Intel’s Atlas project, which records cryptographically verifiable metadata across the entire ML lifecycle, from dataset prep to inference. Combined with Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) and transparency logs, Atlas enables machine-verifiable claims about model lineage and integrity.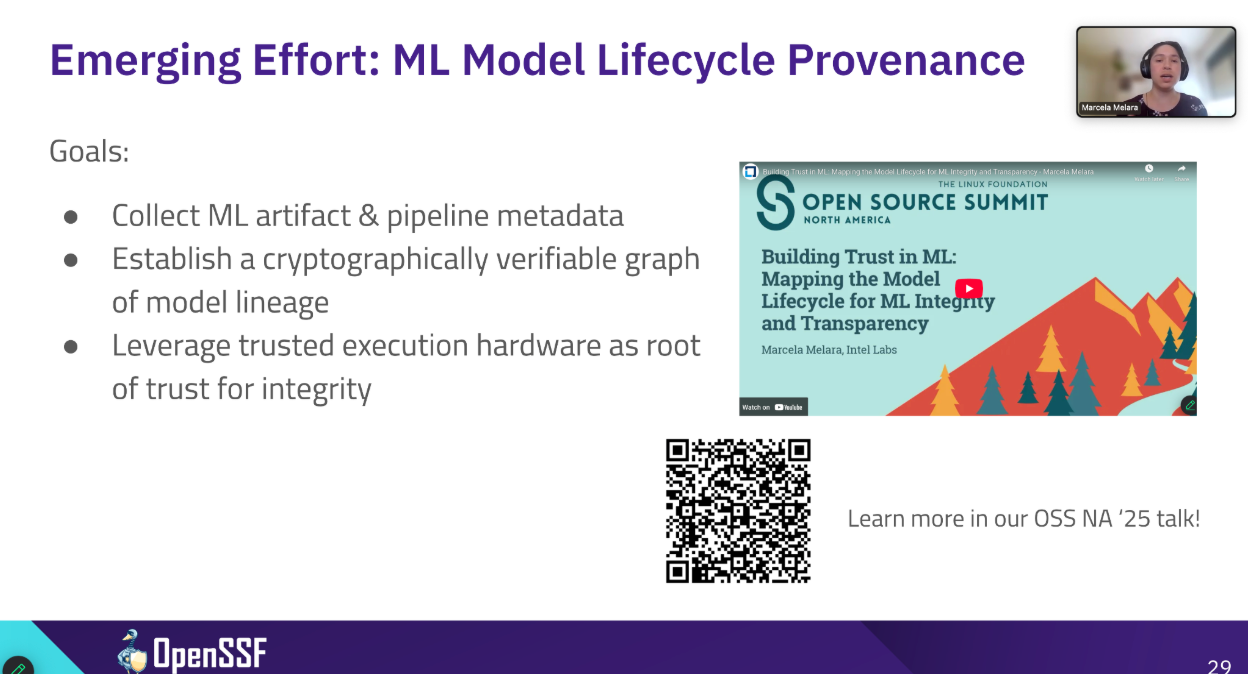
- Emerging GPU-Based Integrity
New research leverages GPUs for high-performance hashing and signing, uniting confidential VMs and secure CPU↔GPU communication standards to accelerate large-scale AI integrity operations. - AI/ML “SBOMs”
The panel discussed how software bill of materials (SBOM) concepts are evolving for AI, with SPDX 3.0 introducing model and data profiles, and CycloneDX working on parallel specifications. Long-term vision: automatically generate AI BOMs from ingested provenance. - Privacy & Risk Guidance
Recommendations included threat modeling by use case, applying controls from MITRE, Cloud Security Alliance, and OWASP AI risk frameworks, and considering confidential computing or contractual safeguards when handling sensitive data. - New Learning Resources
Dr. David A. Wheeler announced the release of:- New OpenSSF Guidance on AI Code Assistant Instructions
- A free course, Secure AI/ML-Driven Software Development (LFEL1012), launching October 16. Fill in the interest form and sign-up for launch notification.
- New AIML Special Interest Groups
The AIML panelists expressed excitement about two new promising Special Interest groups under the umbrella AIML Working Group: Cyber Reasoning Systems (engage with teams that participated in DARPA’s AIxCC challenge that will be open sourcing their cyber reasoning systems) and Safe MCP (a Security Analysis Framework for Evaluation of Model Context Protocol (MCP)).
Call to Action
The discussion closed with a strong message: community collaboration is key. OpenSSF invites developers, researchers, and practitioners to:
- Join the AI/ML Security Working Group!
- Explore the MLSecOps whitepaper: Visualizing Secure MLOps (MLSecOps): A Practical Guide for Building Robust AI/ML Pipeline Security
- Try the Model Signing tools.
- Contribute to OpenSSF Model Signing Specification for AI provenance and SBOMs.
As AI continues to reshape how software is built and deployed, securing its lifecycle requires open collaboration, shared tooling, and transparency at every stage.
To get involved, visit openssf.org and join the conversation on Slack, GitHub, and upcoming community events.